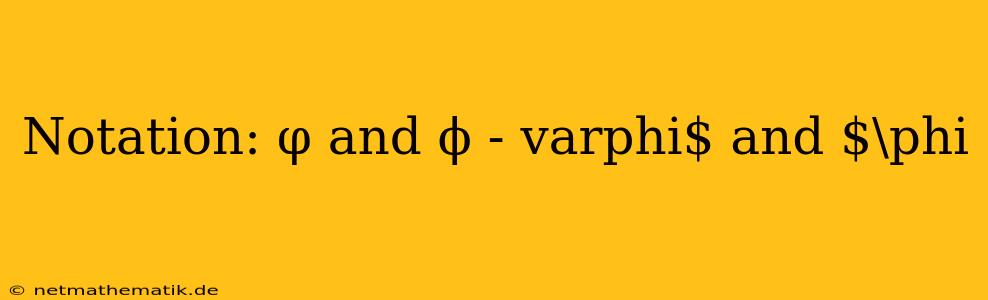The Greek letter phi (Φ, φ, or ϕ) is a symbol used in mathematics, physics, and other fields. It can represent different concepts and quantities depending on the context. While the two forms, φ and ϕ, appear similar, they are often used interchangeably and can be distinguished based on the font style or context. In mathematical texts, the form "φ" is more commonly used, while the form "ϕ" is more frequently used in physics and other fields. This article explores the different applications of phi (φ and ϕ) and highlights its significance in various domains.
The Golden Ratio: Φ, φ, or ϕ
One of the most prominent uses of phi is in the representation of the golden ratio, often denoted as Φ (uppercase phi). The golden ratio is an irrational number approximately equal to 1.618. It is often defined as the ratio of a line segment divided into two parts such that the longer part divided by the shorter part is equal to the whole length divided by the longer part. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
a/b = (a + b)/a = Φ
Where "a" represents the longer segment and "b" represents the shorter segment.
The golden ratio appears in various natural phenomena, including the spiral arrangement of seeds in a sunflower, the branching patterns in trees, and the proportions of the human body. Its mathematical properties have also inspired artists, architects, and designers for centuries, leading to the incorporation of the golden ratio in works of art, architecture, and design.
Phi in Geometry and Trigonometry
In geometry and trigonometry, phi (φ) is frequently used to represent an angle. This usage stems from its association with the unit circle, where an angle is typically measured from the positive x-axis counterclockwise.
φ can be expressed in degrees or radians. In a unit circle, where the radius is 1, the angle φ corresponds to the arc length of the circle.
φ is also used in spherical coordinates, where it represents the azimuthal angle. The azimuthal angle is the angle measured from a reference direction, typically the positive x-axis, in a plane perpendicular to the z-axis.
Phi in Physics
In physics, phi (φ) is used to represent various quantities, including:
-
Electric potential: In electromagnetism, phi (φ) is often used to represent the electric potential at a point in space. Electric potential is a scalar quantity that describes the potential energy per unit charge at a given location.
-
Magnetic flux: In magnetism, phi (φ) can represent the magnetic flux through a surface. Magnetic flux is a measure of the amount of magnetic field lines passing through a surface.
-
Phase: In wave physics, phi (φ) represents the phase of a wave. Phase is a measure of the position of a point in a wave cycle relative to a reference point.
Phi in Other Fields
Beyond mathematics and physics, phi (φ) finds applications in various other fields, including:
-
Computer science: In computer science, phi (φ) is used in cryptography and data compression algorithms.
-
Finance: In finance, phi (φ) can be used to represent risk aversion in portfolio optimization.
-
Linguistics: In linguistics, phi (φ) is sometimes used to represent the phonological feature of voicelessness.
Conclusion
The Greek letter phi (Φ, φ, or ϕ) plays a significant role in various fields, representing diverse concepts and quantities. From the golden ratio in mathematics to electric potential and magnetic flux in physics, phi (φ) demonstrates its versatility and importance in diverse scientific and technical disciplines. The distinction between φ and ϕ often depends on the context and font style, but both forms are widely accepted and used interchangeably in various applications. Whether it's representing angles, ratios, or other physical quantities, phi (φ) remains a crucial symbol in scientific notation and understanding.